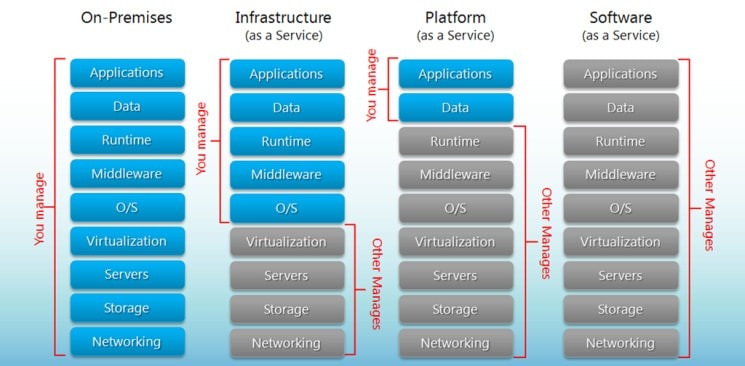
Types of Cloud Services
SaaS
Software as a Service
Cloud-based service providers offer end-user applications. Google Apps, DropBox, Slack, etc.
Web access to Software (primarily commercial).
Software is managed from a central location.
Delivery 1 - many models.
No patches, No upgrades
When not to use
Hardware integration is needed. (Price Scanner)
Faster processing is required.
Cannot host data outside the premise.
PaaS
Platform as a Service
Software tools are available over the internet. AWS RDS, Heroku, Salesforce
Scalable
Built on Virtualization Technology
No User needed to maintain software. (DB upgrades, patches by cloud team)
When not to use PaaS
Propriety tools don't allow moving to diff providers. (AWS-specific tools)
Using new software that is not part of the PaaS toolset.
IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service
Cloud-based hardware services. Pay-as-you-go services for Storage, Networking, and Servers.
Amazon EC2, Google Compute Engine, S3.
Highly flexible and scalable.
Accessible by more than one user.
Cost-effective (if used right).
FaaS - Serverless computing
Function as a Service.
Focuses on building apps without spending time managing servers/infrastructure.
It features automatic scaling, built-in high availability, and pay-per-use.
Use of resources when a specific function or event occurs.
Cloud providers handle the deployment and capacity of servers and manage them.
Example: Azure Functions, AWS Lambda, AWS Step Functions.
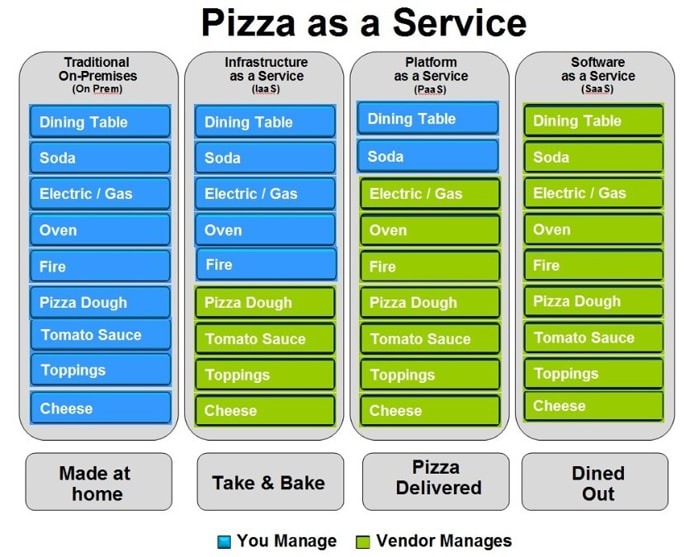
Easy way to remember SaaS, PaaS, IaaS
Last updated